gmt.conf¶
Configuration for GMT
Description¶
The following is a list of the parameters that are user-definable in GMT. The parameter names are always given in UPPER CASE. The parameter values are case-insensitive unless otherwise noted. Theme-independent system defaults are given in brackets [default is value], with units specified for dimensional quantities, while theme-dependent defaults are outlined in the GMT_THEME settings table. Most parameters can be changed by using gmtset, editing a gmt.conf file that can be acquired using gmtdefaults, or setting parameters on-the-fly via the --PARAMETER=VALUE option to any GMT program. However, a few are static and are only read via the gmt.conf file; these are labeled (static). Several parameters take only true or false. It is recommended that users specify the units for distances and lengths by appending c (cm), i (inch), or p (points) when changing parameters using any of these methods. By default, when no unit is specified the value will be assumed to be cm for parameters not related to fonts or pen thicknesses and will be assumed to be points for parameters related to fonts or pen thicknesses. The interpretation of unitless dimensional quantities can be changed using the parameter PROJ_LENGTH_UNIT or specifying US units when building GMT.
Common Specifications¶
The full explanation for how to specify pens, pattern fills, colors, and fonts can be found in the gmt man page.
THEMATIC SUB-SECTIONS |
prefix |
|---|---|
COLOR_ |
|
DIR_ |
|
FONT_ |
|
FORMAT_ |
|
GMT_ |
|
IO_ |
|
MAP_ |
|
PROJ_ |
|
PS_ |
|
TIME_ |
COLOR Parameters¶
- COLOR_BACKGROUND¶
Color used for the background of images (i.e., when z < lowest color table entry) [default is black].
- COLOR_FOREGROUND¶
Color used for the foreground of images (i.e., when z > highest color table entry) [default is white].
- COLOR_CPT¶
Default CPT table when none is selected [default is turbo].
- COLOR_HSV_MAX_S¶
Maximum saturation (0-1) assigned for most positive intensity value [default is 0.1].
- COLOR_HSV_MIN_S¶
Minimum saturation (0-1) assigned for most negative intensity value [default is 1.0].
- COLOR_HSV_MAX_V¶
Maximum value (0-1) assigned for most positive intensity value [default is 1.0].
- COLOR_HSV_MIN_V¶
Minimum value (0-1) assigned for most negative intensity value [default is 0.3].
- COLOR_MODEL¶
Selects in which color space a CPT should be interpolated. By default, color interpolation takes place directly on the RGB values which can produce some unexpected hues, whereas interpolation directly on the HSV values better preserves those hues. The choices are: none (use whatever the COLOR_MODEL setting in the CPT demands), rgb (force interpolation in RGB), hsv (force interpolation in HSV), cmyk (assumes colors are in CMYK but interpolates in RGB) [default is none].
- COLOR_NAN¶
Color used for the non-defined areas of images (i.e., where z = NaN) [default is 128].
- COLOR_SET¶
Default comma-separated list of colors (or a categorical CPT name) for automatic, sequential color assignments [default is #0072BD,#D95319,#EDB120,#7E2F8E,#77AC30,#4DBEEE,#A2142F].
DIR Parameters¶
- DIR_CACHE¶
Cache directory where we save remote filenames starting in @ (e.g., @hotspots.txt) [default is ~/.gmt/cache].
- DIR_DATA¶
Session data directory. Overrides the value of the environment variable $GMT_DATADIR (see Directory parameters in the CookBook).
- DIR_DCW¶
Path to optional Digital Chart of the World polygon files.
- DIR_GSHHG¶
Path to GSHHG files. Defaults to $GMT_SHAREDIR/coast if empty.
FONT Parameters¶
- FONT¶
Sets the default for all fonts, except FONT_LOGO. This setting is not included in the gmt.conf file.
- FONT_ANNOT¶
Sets both FONT_ANNOT_PRIMARY and FONT_ANNOT_SECONDARY to the value specified. This setting is not included in the gmt.conf file.
- FONT_ANNOT_PRIMARY¶
Font used for primary annotations, etc [default is theme dependent]. When + is prepended, scale fonts, offsets and tick-lengths relative to FONT_ANNOT_PRIMARY. Choose auto for automatic scaling with plot size.
- FONT_ANNOT_SECONDARY¶
Font to use for time axis secondary annotations [default is theme dependent] Choose auto for automatic scaling with plot size.
- FONT_HEADING¶
Font to use when plotting headings above subplots [default is theme dependent]. Choose auto for automatic scaling with plot size.
- FONT_LABEL¶
Font to use when plotting labels below axes [default is theme dependent]. Choose auto for automatic scaling with plot size.
- FONT_LOGO¶
Font to use for text plotted as part of the GMT time logo [theme dependent]. Choose auto for automatic scaling with plot size.
- FONT_SUBTITLE¶
Font to use when plotting titles over graphs that involve a subtitle [default is theme dependent]. Choose auto for automatic scaling with plot size.
- FONT_TAG¶
Font to use for subplot panel tags such as a), ii) [default is theme dependent]. Choose auto for automatic scaling with plot size.
- FONT_TITLE¶
Font to use when plotting titles over graphs [default is theme dependent]. Choose auto for automatic scaling with plot size.
FORMAT Parameters¶
- FORMAT_CLOCK_IN¶
Formatting template that indicates how an input clock string is formatted. This template is then used to guide the reading of clock strings in data fields. To properly decode 12-hour clocks, append am or pm (or upper case) to match your data records. As examples, try hh:mm, hh:mm:ssAM, etc. [default is hh:mm:ss].
- FORMAT_CLOCK_MAP¶
Formatting template that indicates how an output clock string is to be plotted. This template is then used to guide the formatting of clock strings in plot annotations. See FORMAT_CLOCK_OUT for details. [default is hh:mm:ss].
- FORMAT_CLOCK_OUT¶
Formatting template that indicates how an output clock string is to be formatted. This template is then used to guide the writing of clock strings in data fields. To use a floating point format for the smallest unit (e.g., seconds), append .xxx, where the number of x indicates the desired precision. If no floating point is indicated then the smallest specified unit will be rounded off to nearest integer. For 12-hour clocks, append am, AM, a.m., or A.M. (GMT will replace a|A with p|P for pm). If your template starts with a leading hyphen (-) then each integer item (y,m,d) will be printed without leading zeros (default uses fixed width formats). As examples, try hh:mm, hh.mm.ss, hh:mm:ss.xxxx, hha.m., etc. [default is hh:mm:ss]. If the format is simply - then no clock is output and the ISO T divider between date and clock is omitted. Note: When high-precision time-series are written to ASCII output the default format may not be adequate. Many modules automatically handle this by extending the format, but you should be alert of unusual situations where data may appear truncated to nearest second.
- FORMAT_DATE_IN¶
Formatting template that indicates how an input date string is formatted. This template is then used to guide the reading of date strings in data fields. You may specify either Gregorian calendar format or ISO week calendar format. Gregorian calendar: Use any combination of yyyy (or yy for 2-digit years; if so see TIME_Y2K_OFFSET_YEAR), mm (or o for abbreviated month name in the current time language), and dd, with or without delimiters. For day-of-year data, use jjj instead of mm and/or dd. Examples can be ddmmyyyy, yy-mm-dd, dd-o-yyyy, yyyy/dd/mm, yyyy-jjj, etc. ISO Calendar: Expected template is yyyy[-]W[-]ww[-]d, where ww is ISO week and d is ISO week day. Either template must be consistent, e.g., you cannot specify months if you do not specify years. Examples are yyyyWwwd, yyyy-Www, etc. [default is yyyy-mm-dd].
- FORMAT_DATE_MAP¶
Formatting template that indicates how an output date string is to be plotted. This template is then used to guide the plotting of date strings in data fields. See FORMAT_DATE_OUT for details. In addition, you may use a single o instead of mm (to plot month name) and u instead of W[-]ww to plot “Week ##”. Both of these text strings will be affected by the GMT_LANGUAGE, FORMAT_TIME_PRIMARY_MAP and FORMAT_TIME_SECONDARY_MAP setting. [default is yyyy-mm-dd].
- FORMAT_DATE_OUT¶
Formatting template that indicates how an output date string is to be formatted. This template is then used to guide the writing of date strings in data fields. You may specify either Gregorian calendar format or ISO week calendar format. Gregorian calendar: Use any combination of yyyy (or yy for 2-digit years; if so see TIME_Y2K_OFFSET_YEAR), mm (or o for abbreviated month name in the current time language), and dd, with or without delimiters. For day-of-year data, use jjj instead of mm and/or dd. As examples, try yy/mm/dd, yyyy=jjj, dd-o-yyyy, dd-mm-yy, yy-mm, etc. ISO Calendar: Expected template is yyyy[-]W[-]ww[-]d, where ww is ISO week and d is ISO week day. Either template must be consistent, e.g., you cannot specify months if you do not specify years. As examples, try yyyyWww, yy-W-ww-d, etc. If your template starts with a leading hyphen (-) then each integer item (y,m,d) will be printed without leading zeros (default uses fixed width formats) [default is yyyy-mm-dd]. If the format is simply - then no date is output and the ISO T divider between date and clock is omitted.
- FORMAT_GEO_MAP¶
Formatting template that indicates how an output geographical coordinate is to be plotted. This template is then used to guide the plotting of geographical coordinates in data fields. See FORMAT_GEO_OUT for details. In addition, you can append A which plots the absolute value of the coordinate. Not all items may be plotted as this depends on the annotation interval. [default is theme dependent].
- FORMAT_GEO_OUT¶
Formatting template that indicates how an output geographical coordinate is to be formatted. This template is then used to guide the writing of geographical coordinates in data fields. The template is in general of the form [±]D or [±]ddd[:mm[:ss]][.xxx] [default is D]. By default, longitudes will be reported in the range [-180,180]. The various terms have the following purpose:
Term
Purpose
D
Use FORMAT_FLOAT_OUT for floating point degrees [default]
+D
Output longitude in the range [0,360]
-D
Output longitude in the range [-360,0]
ddd
Fixed format integer degrees
:
Delimiter used
mm
Fixed format integer arc minutes
ss
Fixed format integer arc seconds
.xxx
Floating fraction of previous integer field, fixed width
F
Encode sign using WESN suffix
G
Same as F but with a leading space before suffix
- FORMAT_FLOAT_MAP¶
Format (C language printf syntax, see FORMAT_FLOAT_OUT) to be used when plotting double precision floating point numbers along plot frames and contours. For geographic coordinates, see FORMAT_GEO_MAP. [default is %.12g].
- FORMAT_FLOAT_OUT¶
Format (C language printf syntax) to be used when printing double precision floating point numbers to output files. For geographic coordinates, see FORMAT_GEO_OUT. [default is %.12g]. To give some columns a separate format, supply one or more comma-separated cols:format specifications, where cols can be specific columns (e.g., 5 for 6th since 0 is the first) or a range of columns (e.g., 3-7). The last specification without column information will override the format for all other columns. Alternatively, you can list N space-separated formats and these apply to the first N columns.
The printf syntax is
%[minimum width].[precision]type, where type may be f, e, E, g or G. The default is%.12g, i.e. no minimum width and 12 digit precisision.- FORMAT_TIME_MAP¶
Sets both FORMAT_TIME_PRIMARY_MAP and FORMAT_TIME_SECONDARY_MAP to the value specified. This setting is not included in the gmt.conf file.
- FORMAT_TIME_PRIMARY_MAP¶
Controls how primary month-, week-, and weekday-names are formatted. Choose among full, abbreviated, and character. If the leading f, a, or c are replaced with F, A, and C the entire annotation will be in upper case [default is full].
- FORMAT_TIME_SECONDARY_MAP¶
Controls how secondary month-, week-, and weekday-names are formatted. Choose among full, abbreviated, and character. If the leading f, a, or c are replaced with F, A, and C the entire annotation will be in upper case [default is full].
- FORMAT_TIME_STAMP¶
Defines the format of the time information in the UNIX time stamp. This format is parsed by the C function strftime, so that virtually any text can be used (even not containing any time information) [default is %Y %b %d %H:%M:%S].
GMT Miscellaneous Parameters¶
- GMT_COMPATIBILITY¶
Determines if the current GMT version should be able to parse command-line options for a prior major release. Specify the major release version number, e.g., 4-6. If 4 is set we will parse obsolete GMT 4 options and issue warnings; if 5 is set then parsing GMT 4 only syntax will result in errors [default is 4]; likewise for 6: obsolete syntax from early GMT 5 will be considered errors.
- GMT_DATA_SERVER¶
Name (or URL) of a GMT data server [default is oceania]. Please set to the data server closest to your location for faster data download. See Data Server Mirrors for a list of the currently available mirrors.
- GMT_DATA_SERVER_LIMIT¶
Upper limit on the size of remote file to download [default is unlimited]. Give the maximum file size in bytes, or append k, m, or g for kilo-, mega-, or giga-bytes.
- GMT_DATA_UPDATE_INTERVAL¶
Specifies how often we update the local catalog of data available on the remote server and pruning expired data sets [default is 1d]. Allowable time units are d (days), w (week), o (month, here 30 days). To turn off periodic updates entirely, specify interval as off, never, infinity, or just 0.
- GMT_EXPORT_TYPE¶
This setting is only used by external interfaces and controls the data type used for table entries. Choose from double, single, [u]long, [u]int, [u]short, and [u]char [default is double].
- GMT_EXTRAPOLATE_VAL¶
Determines what to do if extrapolating beyond the data domain. Choose among NaN, extrap or extrapval,value. In the first case return NaN for any element of x that is outside range. Second case lets the selected algorithm compute the extrapolation values. Third case sets the extrapolation values to the constant value passed in value (this value must off course be numeric) [default is NaN].
- GMT_CUSTOM_LIBS¶
Comma-separated list of GMT-compliant shared libraries that extend the capability of GMT with additional custom modules [default is none]. Alternatively, provide a directory name, that MUST end with a slash (or back slash), to use all shared libraries in that directory. On Windows, if the dir name is made up only of a single slash (‘/’) search inside a subdirectory called gmt_plugins of the directory that contains the gmt executable. See the API documentation for how to build your own shared modules.
- GMT_FFT¶
Determines which Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) should be used among those that have been configured during installation. Choose from auto (pick the most suitable for the task among available algorithms), fftw[,planner_flag] (The Fastest Fourier Transform in the West), accelerate (Use the Accelerate Framework under OS X; Note, that the number of samples to be processed must be a base 2 exponent), kiss, (Kiss FFT), brenner Brenner Legacy FFT [default is auto]. FFTW can “learn” how to optimally compute Fourier transforms on the current hardware and OS by computing several FFTs and measuring their execution time. This so gained “Wisdom” will be stored in and reloaded from the file fftw_wisdom_<hostname> in $GMT_USERDIR or, if $GMT_USERDIR is not writable, in the current directory. To use this feature append planner_flag, which can be one of measure, patient, exhaustive and estimate which pick a (probably sub-optimal) plan quickly [default is estimate]. See FFTW reference for details. Note: If you need a single transform of a given size only, the one-time cost of the smart planner becomes significant. In that case, stick to the default planner, estimate, based on heuristics.
- GMT_GRAPHICS_FORMAT¶
Default graphics format in modern mode [default is pdf].
- GMT_HISTORY¶
Passes the history of past common command options via the gmt.history file. The different values for this setting are: true, readonly, false, to either read and write to the gmt.history file, only read, or not use the file at all [default is true].
- GMT_INTERPOLANT¶
Determines if linear (linear), Akima’s spline (akima), natural cubic spline (cubic) or no interpolation (none) should be used for 1-D interpolations in various programs [default is akima].
- GMT_LANGUAGE¶
Language to use when plotting calendar and map items such as months and days, map annotations and cardinal points. Select from:
CN1: Simplified Chinese
CN2: Traditional Chinese
DE: German
DK: Danish
EH: Basque
ES: Spanish
FI: Finnish
FR: French
GR: Greek
HI: Hawaiian
HU: Hungarian
IE: Irish
IL: Hebrew
IS: Icelandic
IT: Italian
JP: Japanese
KR: Korean
NL: Dutch
NO: Norwegian
PL: Polish
PT: Portuguese
RU: Russian
SE: Swedish
SG: Scottish Gaelic
TO: Tongan
TR: Turkish
UK: British English
US: US English
If your language is not supported, please examine the $GMT_SHAREDIR/localization/gmt_us.locale file and make a similar file. Please submit it to the GMT Developers for official inclusion. Custom language files can be placed in directories $GMT_SHAREDIR/localization or ~/.gmt. Note: Some of these languages may require you to also change the PS_CHAR_ENCODING setting.
- GMT_MAX_CORES¶
Sets the upper limit on the number of cores any multi-threaded module might use (whether -x is selected or not) [default is 0 (i.e., unlimited)].
- GMT_THEME¶
Override GMT default settings with those of the selected theme. Choose from classic [Default for classic mode], modern [Default for modern mode], and minimal. You can also create and use your own themes by compiling files of desired settings and place them in your GMT user themes directory (usually ~/.gmt/themes) and name them theme.conf. See the theme settings table for parameters associated with each theme.
- GMT_TRIANGULATE¶
Determines if we use the Watson or Shewchuk algorithm (if configured during installation) for triangulation. Note that Shewchuk is required for operations involving Voronoi constructions [default is Watson].
- GMT_VERBOSE¶
(-V) Determines the level of verbosity used by GMT programs. Choose among 7 levels; each level adds to the verbosity of the lower levels: quiet, errors, warnings, timings (for slow algorithms only), information, compatibility warnings, and debugging messages [default is w].
I/O Parameters¶
- IO_COL_SEPARATOR¶
This setting determines what character will separate ASCII output data columns written by GMT. Choose from tab, space, comma, and none [default is tab].
- IO_FIRST_HEADER¶
This setting determines if the first segment header is written when there is only a single segment (for multiple segment it must be written). By default, such single-segment headers are only written if the header has contents. Choose from always, never, or maybe [default is maybe].
- IO_GRIDFILE_FORMAT¶
Default file format for grids, with optional scale, offset and invalid value, written as ff[+sscale][+ooffset][+ninvalid]. The 2-letter format indicator can be one of [abcegnrs][bsifd]. See grdconvert and Section Grid file format specifications of the GMT Technical Reference and Cookbook for more information. You may the scale as a for auto-adjusting the scale and/or offset of packed integer grids (=ID+sa is a shorthand for =ID+sa+oa). When invalid is omitted the appropriate value for the given format is used (NaN or largest negative) [default is nf].
- IO_GRIDFILE_SHORTHAND¶
If true, all grid file names are examined to see if they use the file extension shorthand discussed in Section Grid file format specifications of the GMT Technical Reference and Cookbook. If false, no filename expansion is done [default is false].
- IO_HEADER¶
(-h) Specifies whether input/output ASCII files have header record(s) or not [default is false].
- IO_HEADER_MARKER¶
Give a string from which any character will indicate a header record in an incoming ASCII data table if found in the first position [default is #%!;”’]. If another marker should be used for output than the first character in the list, then append a single character for the output header record marker. The two sets must be separated by a comma. Note: A maximum of 7 input markers can be specified.
- IO_LONLAT_TOGGLE¶
(-:) Set if the first two columns of input and output files contain (latitude,longitude) or (y,x) rather than the expected (longitude,latitude) or (x,y). false means we have (x,y) both on input and output. true means both input and output should be (y,x). IN means only input has (y,x), while OUT means only output should be (y,x) [default is false].
- IO_N_HEADER_RECS¶
Specifies how many header records to expect if -h is used [default is 0]. Note: This will skip the specified number of records regardless of what they are. Since any records starting with # is automatically considered a header you will only specify a non-zero number in order to skip headers that do not conform to that convention.
- IO_NAN_RECORDS¶
Determines what happens when input records containing NaNs for x or y (and in some cases z) are read. This may happen, for instance, when there is text or other junk present instead of data coordinates, and the conversion to a data value fails and yields a NaN. Choose between skip, which will report how many bad records were skipped, and pass, which will quietly pass these records on to the calling programs [default is pass]. For most programs this will result in output records with NaNs as well, but some will interpret these NaN records to indicate gaps in a series; programs may then use that information to detect segmentation (if applicable).
- IO_NC4_CHUNK_SIZE¶
Sets the default chunk size for the vertical (lat, y) and horizontal (lon, x) dimensions of the z variable. Very large chunk sizes and sizes smaller than 128 should be avoided because they can lead to unexpectedly bad performance. Note that a chunk of a single precision floating point variable of size 2896x2896 completely fills the chunk cache of 32 MiB. Specify the chunk size for each dimension separated by a comma, or auto for optimally chosen chunk sizes in the range [128,256). Setting IO_NC4_CHUNK_SIZE will produce netCDF version 4 files, which can only be read with the netCDF 4 library, unless all dimensions are less than 128 or classic is specified for classic netCDF [default is auto]
- IO_NC4_DEFLATION_LEVEL¶
Sets the compression level for netCDF4 files upon output. Values allowed are integers from 0 (no compression) to 9 (maximum compression). Enabling a low compression level can dramatically improve performance and reduce the size of certain data. While higher compression levels further reduce the data size, they do so at the cost of extra processing time. This parameter does not apply to classic netCDF files [default is 3].
- IO_SEGMENT_BINARY¶
Determines how binary data records with all values set to NaN are interpreted. Such records are considered to be encoded segment headers in binary files provided the number of columns equals or exceeds the current setting of IO_SEGMENT_BINARY [default is 2]. Specify 0 or off to deactivate the segment header determination.
- IO_SEGMENT_MARKER¶
This holds the character we expect to indicate a segment header in an incoming ASCII data or text table [default is >]. If this marker should be different for output then append another character for the output segment marker. The two characters must be separated by a comma. Two marker characters have special meaning: B means “blank line” and will treat blank lines as initiating a new segment, whereas N means “NaN record” and will treat records with all NaNs as initiating a new segment. If you choose B or N for the output marker then the normal GMT segment header is replaced by a blank or NaN record, respectively, and no segment header information is written. To use B or N as regular segment markers you must escape them with a leading backslash.
MAP Parameters¶
- MAP_ANNOT_MIN_ANGLE¶
If the angle between the map boundary and the annotation baseline is less than this minimum value (in degrees), the annotation is not plotted (this may occur for certain oblique projections). Give a value in the range [0,90] [default is 20].
- MAP_ANNOT_MIN_SPACING¶
If an annotation would be plotted less than this minimum distance from its closest neighbor, the annotation is not plotted (this may occur for certain oblique or polar projections) [default is theme dependent]. Choose auto for automatic scaling with plot size.
- MAP_ANNOT_OBLIQUE¶
This argument is a comma-separated list of up to seven keywords: separate means longitudes will be annotated on the lower and upper boundaries only, and latitudes will be annotated on the left and right boundaries only; anywhere means annotations will occur wherever an imaginary gridline crosses the map boundaries; lon_horizontal means longitude annotations will be plotted horizontally; lat_horizontal means latitude annotations will be plotted horizontally; tick_extend means tick-marks are extended so the distance from the tip of the oblique tick to the map frame equals the specified tick length; tick_normal means tick-marks will be drawn normal to the border regardless of gridline angle; lat_parallel means latitude annotations will be plotted parallel to the border [default is anywhere].
- MAP_ANNOT_OFFSET¶
Sets both MAP_ANNOT_OFFSET_PRIMARY and MAP_ANNOT_OFFSET_SECONDARY to the value specified. This setting is not included in the gmt.conf file.
- MAP_ANNOT_OFFSET_PRIMARY¶
Distance from end of tick-mark to start of annotation [default is theme dependent]. Choose auto for automatic scaling with plot size.
- MAP_ANNOT_OFFSET_SECONDARY¶
Distance from base of primary annotation to the top of the secondary annotation (Only applies to time axes with both primary and secondary annotations) [default is theme dependent]. Choose auto for automatic scaling with plot size.
- MAP_ANNOT_ORTHO¶
Determines which axes will get their annotations (for Cartesian projections) plotted orthogonally to the axes. Combine any w, e, s, n, z (uppercase allowed as well) [default is we] (if nothing specified). Note that this setting can be overridden via the +a modifier in -B.
- MAP_DEFAULT_PEN¶
Sets the default of all pens related to -W options. Prepend + to overrule the color of the parameters MAP_GRID_PEN_PRIMARY, MAP_GRID_PEN_SECONDARY, MAP_FRAME_PEN, MAP_TICK_PEN_PRIMARY, and MAP_TICK_PEN_SECONDARY by the color of MAP_DEFAULT_PEN [default is 0.25p,black].
- MAP_DEGREE_SYMBOL¶
Determines what symbol is used to plot the degree symbol on geographic map annotations. Choose between ring, degree, colon, or none [default is degree].
- MAP_FRAME_AXES¶
Sets which axes to draw and annotate. Combine any uppercase W, E, S, N, Z to draw and annotate west, east, south, north and/or vertical (perspective view only) axis. Use lower case to draw the axis only, but not annotate. To just draw an axis without annotation and ticks you can use the l(eft), r(ight), b(ottom), t(op) and (for 3-D) u(p) codes. Add an optional +b to draw a cube of axes in perspective view. Choose auto for automatic selection [default is theme dependent].
- MAP_FRAME_PEN¶
Pen attributes used to draw plain map frame [default is theme dependent]. Choose auto for automatic scaling with plot size.
- MAP_FRAME_PERCENT¶
Percentage of the fancy frame width to use for the internal checkerboard frame lines [default is 100].
- MAP_FRAME_TYPE¶
Choose between inside, plain and fancy (thick boundary, alternating black/white frame; append -rounded for rounded corners) [default is theme dependent]. For some map projections (e.g., Oblique Mercator), plain is the only option even if fancy is set as default. In general, fancy only applies to situations where the projected x and y directions parallel the longitude and latitude directions (e.g., rectangular projections, polar projections). For situations where all boundary ticks and annotations must be inside the maps (e.g., for preparing geotiffs), chose inside. Finally, for Cartesian plots you can also choose graph, which adds a vector to the end of each axis. This works best when you reduce the number of axes plotted to one per dimension. By default, the vector tip extends the length of each axis by 7.5%. Alternatively, append ,length, where the optional unit may be % (then length is the alternate extension in percent) or one of c, i, or p (then length is the absolute extension of the axis to the start of the vector base instead). The vector stem is set to match MAP_FRAME_WIDTH, while the vector head length and width are 10 and 5 times this width, respectively. You may control its shape via MAP_VECTOR_SHAPE.
Here is an example showing the appearance of different MAP_FRAME_TYPE settings.
gmt begin GMT_map_frame_type gmt set GMT_THEME cookbook gmt set FONT_TITLE 18p gmt subplot begin 1x5 -Fs3.5c/3.5c -M0.4c -R0/10/0/10 gmt basemap -JM? -Baf -BWSen+t"fancy" -c --MAP_FRAME_TYPE=fancy gmt basemap -JM? -Baf -BWSen+t"fancy+" -c --MAP_FRAME_TYPE=fancy+ gmt basemap -JM? -Baf -BWSen+t"plain" -c --MAP_FRAME_TYPE=plain gmt basemap -JX? -Baf -BWSen+t"inside" -c --MAP_FRAME_TYPE=inside gmt basemap -JX? -Baf -BWS+t"graph" -c --MAP_FRAME_TYPE=graph gmt subplot end gmt end show
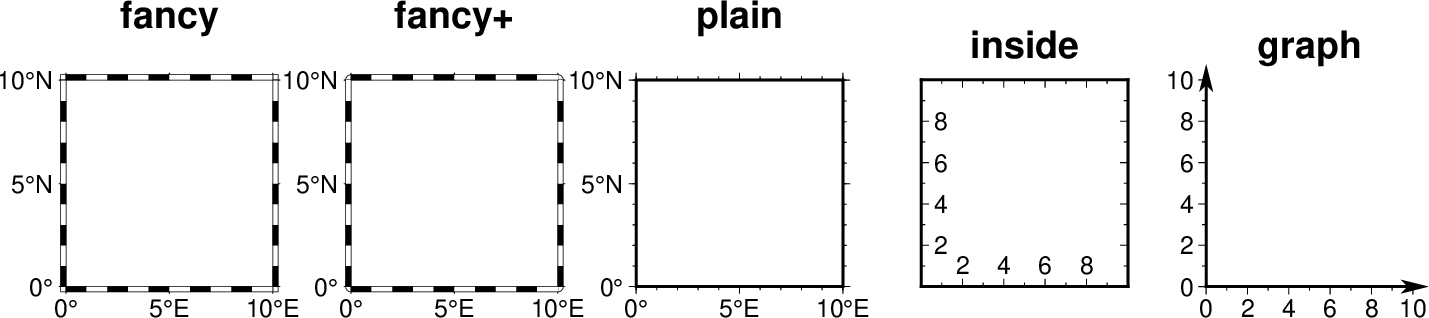
Appearance of different MAP_FRAME_TYPE settings¶
- MAP_FRAME_WIDTH¶
Width (> 0) of map borders for fancy map frame [default is theme dependent]. Note: For fancy frames, MAP_FRAME_PEN is automatically set to 0.1 times the MAP_FRAME_WIDTH setting. Choose auto for automatic scaling with plot size.
- MAP_GRID_CROSS_SIZE¶
Sets both MAP_GRID_CROSS_SIZE_PRIMARY and MAP_GRID_CROSS_SIZE_SECONDARY to the value specified. This setting is not included in the gmt.conf file.
- MAP_GRID_CROSS_SIZE_PRIMARY¶
Size of grid cross at lon-lat intersections. 0 means draw continuous gridlines instead. A nonzero size will draw a symmetric grid cross. Signed sizes have special meaning and imply grid line ticks that embellish an already drawn set of gridlines: A negative size will only draw ticks away from Equator and Greenwich, while a positive size will draw symmetric ticks [default is 0p].
- MAP_GRID_CROSS_SIZE_SECONDARY¶
Size of grid cross at secondary lon-lat intersections. 0 means draw continuous gridlines instead. A nonzero size will draw a symmetric grid cross. Signed sizes have special meaning and imply grid line ticks that embellish an already drawn set of gridlines: A negative size will only draw ticks away from Equator and Greenwich, while a positive size will draw symmetric ticks [default is 0p].
- MAP_GRID_PEN¶
Sets both MAP_GRID_PEN_PRIMARY and MAP_GRID_PEN_SECONDARY to the value specified. This setting is not include in the gmt.conf file.
- MAP_GRID_PEN_PRIMARY¶
Pen attributes used to draw primary grid lines in dpi units or points (append p) [default is theme dependent]. Choose auto for automatic scaling with plot size.
- MAP_GRID_PEN_SECONDARY¶
Pen attributes used to draw secondary grid lines in dpi units or points (append p) [default is theme dependent]. Choose auto for automatic scaling with plot size.
- MAP_HEADING_OFFSET¶
Distance from top of subplot panel titles to the base of the heading [default is theme dependent]. Choose auto for automatic scaling with plot size.
- MAP_LABEL_OFFSET¶
Distance from base of axis annotations to the top of the axis label [default is theme dependent]. Choose auto for automatic scaling with plot size.
- MAP_LINE_STEP¶
Determines the maximum length (> 0) of individual straight line-segments when drawing arcuate lines [default is 0.75p]
- MAP_LOGO¶
(-U) Specifies if a GMT logo with system timestamp should be plotted at the lower left corner of the plot [default is false].
- MAP_LOGO_POS¶
(-U) Sets the justification and the position of the logo/timestamp box relative to the current plot’s lower left corner (i.e., map origin) [default is BL/-54p/-54p].
- MAP_ORIGIN_X¶
(-X) Sets the x-coordinate of the origin on the paper for a new plot [default is 72p]. For an overlay, the default offset is 0.
- MAP_ORIGIN_Y¶
(-Y) Sets the y-coordinate of the origin on the paper for a new plot [default is 72p]. For an overlay, the default offset is 0.
- MAP_POLAR_CAP¶
Controls the appearance of gridlines near the poles for all azimuthal projections and a few others in which the geographic poles are plotted as points (Lambert Conic, Oblique Mercator, Hammer, Mollweide, Sinusoidal and van der Grinten). Specify either none (in which case there is no special handling) or pc_lat/pc_dlon. In that case, normal gridlines are only drawn between the latitudes -pc_lat/+pc_lat, and above those latitudes the gridlines are spaced at the (presumably coarser) pc_dlon interval; the two domains are separated by a small circle drawn at the pc_lat latitude. Alternatively, give auto to determine a pc_lat suitable for your region [default is theme dependent]. Note for r-theta (polar) projection where r = 0 is at the center of the plot the meaning of the cap is reversed, i.e., 85/90 will draw a r = 5 radius circle at the center of the map with less frequent radial lines there.
- MAP_SCALE_HEIGHT¶
Sets the height (> 0) on the map of the map scale bars drawn by various programs [default is 5p].
- MAP_TICK_LENGTH¶
Sets both MAP_TICK_LENGTH_PRIMARY and MAP_TICK_LENGTH_SECONDARY to the value specified. This setting is not included in the gmt.conf file.
- MAP_TICK_LENGTH_PRIMARY¶
The length of a primary major/minor tick-marks [default is theme dependent]. If only the first value is set, the second is assumed to be 50% of the first. Choose auto for automatic scaling with plot size.
- MAP_TICK_LENGTH_SECONDARY¶
The length of a secondary major/minor tick-marks [default is theme dependent]. If only the first value is set, the second is assumed to be 25% of the first. Choose auto for automatic scaling with plot size.
- MAP_TICK_PEN¶
Sets both MAP_TICK_PEN_PRIMARY and MAP_TICK_PEN_SECONDARY to the value specified. This setting is not included in the gmt.conf file.
- MAP_TICK_PEN_PRIMARY¶
Pen attributes to be used for primary tick-marks in dpi units or points (append p) [default is theme dependent]. Choose auto for automatic scaling with plot size.
- MAP_TICK_PEN_SECONDARY¶
Pen attributes to be used for secondary tick-marks in dpi units or points (append p) [default is theme dependent]. Choose auto for automatic scaling with plot size.
- MAP_TITLE_OFFSET¶
Distance from top of axis annotations (or axis label, if present) to base of plot title [default is theme dependent]. Choose auto for automatic scaling with plot size.
- MAP_VECTOR_SHAPE¶
Determines the shape of the head of a vector. Normally (i.e., for vector_shape = 0), the head will be triangular, but can be changed to an arrow (1) or an open V (2). Intermediate settings give something in between. Negative values (up to -2) are allowed as well [default is theme dependent].
Projection Parameters¶
- PROJ_AUX_LATITUDE¶
Only applies when geodesics are approximated by great circle distances on an equivalent sphere. Select from authalic, geocentric, conformal, meridional, parametric, or none (i.e., geodetic) [default is authalic]. When not none we convert any latitude used in the great circle calculation to the chosen auxiliary latitude before doing the distance calculation. See also PROJ_MEAN_RADIUS.
- PROJ_ELLIPSOID¶
The (case sensitive) name of the ellipsoid used for the map projections [WGS-84]. Choose among:
Airy: Applies to Great Britain (1830)
Airy-Ireland: Applies to Ireland in 1965 (1830)
Andrae: Applies to Denmark and Iceland (1876)
APL4.9: Appl. Physics (1965)
ATS77: Average Terrestrial System, Canada Maritime provinces (1977)
Australian: Applies to Australia (1965)
Bessel: Applies to Central Europe, Chile, Indonesia (1841)
Bessel-Namibia: Same as Bessel-Schwazeck (1841)
Bessel-NGO1948: Modified Bessel for NGO 1948 (1841)
Bessel-Schwazeck: Applies to Namibia (1841)
Clarke-1858: Clarke’s early ellipsoid (1858)
Clarke-1866: Applies to North America, the Philippines (1866)
Clarke-1866-Michigan: Modified Clarke-1866 for Michigan (1866)
Clarke-1880: Applies to most of Africa, France (1880)
Clarke-1880-Arc1950: Modified Clarke-1880 for Arc 1950 (1880)
Clarke-1880-IGN: Modified Clarke-1880 for IGN (1880)
Clarke-1880-Jamaica: Modified Clarke-1880 for Jamaica (1880)
Clarke-1880-Merchich: Modified Clarke-1880 for Merchich (1880)
Clarke-1880-Palestine: Modified Clarke-1880 for Palestine (1880)
CPM: Comm. des Poids et Mesures, France (1799)
Delambre: Applies to Belgium (1810)
Engelis: Goddard Earth Models (1985)
Everest-1830: India, Burma, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Thailand (1830)
Everest-1830-Kalianpur: Modified Everest for Kalianpur (1956) (1830)
Everest-1830-Kertau: Modified Everest for Kertau, Malaysia & Singapore (1830)
Everest-1830-Pakistan: Modified Everest for Pakistan (1830)
Everest-1830-Timbalai: Modified Everest for Timbalai, Sabah Sarawak (1830)
Fischer-1960: Used by NASA for Mercury program (1960)
Fischer-1960-SouthAsia: Same as Modified-Fischer-1960 (1960)
Fischer-1968: Used by NASA for Mercury program (1968)
FlatEarth: As Sphere, but implies fast “Flat Earth” distance calculations (1984)
GRS-67: International Geodetic Reference System (1967)
GRS-80: International Geodetic Reference System (1980)
Hayford-1909: Same as the International 1924 (1909)
Helmert-1906: Applies to Egypt (1906)
Hough: Applies to the Marshall Islands (1960)
Hughes-1980: Hughes Aircraft Company for DMSP SSM/I grid products (1980)
IAG-75: International Association of Geodesy (1975)
Indonesian: Applies to Indonesia (1974)
International-1924: Worldwide use (1924)
International-1967: Worldwide use (1967)
Kaula: From satellite tracking (1961)
Krassovsky: Used in the (now former) Soviet Union (1940)
Lerch: For geoid modeling (1979)
Maupertius: Really old ellipsoid used in France (1738)
Mercury-1960: Same as Fischer-1960 (1960)
MERIT-83: United States Naval Observatory (1983)
Modified-Airy: Same as Airy-Ireland (1830)
Modified-Fischer-1960: Applies to Singapore (1960)
Modified-Mercury-1968: Same as Fischer-1968 (1968)
NWL-10D: Naval Weapons Lab (Same as WGS-72) (1972)
NWL-9D: Naval Weapons Lab (Same as WGS-66) (1966)
OSU86F: Ohio State University (1986)
OSU91A: Ohio State University (1991)
Plessis: Old ellipsoid used in France (1817)
SGS-85: Soviet Geodetic System (1985)
South-American: Applies to South America (1969)
Sphere: The mean radius in WGS-84 (for spherical/plate tectonics applications) (1984)
Struve: Friedrich Georg Wilhelm Struve (1860)
TOPEX: Used commonly for altimetry (1990)
Walbeck: First least squares solution by Finnish astronomer (1819)
War-Office: Developed by G. T. McCaw (1926)
WGS-60: World Geodetic System (1960)
WGS-66: World Geodetic System (1966)
WGS-72: World Geodetic System (1972)
WGS-84: World Geodetic System [Default] (1984)
Web-Mercator: Spherical Mercator with WGS-84 radius (1984)
Moon: Moon (IAU2000) (2000)
Mercury: Mercury (IAU2000) (2000)
Venus: Venus (IAU2000) (2000)
Mars: Mars (IAU2000) (2000)
Jupiter: Jupiter (IAU2000) (2000)
Saturn: Saturn (IAU2000) (2000)
Uranus: Uranus (IAU2000) (2000)
Neptune: Neptune (IAU2000) (2000)
Pluto: Pluto (IAU2000) (2000)
Note that for some global projections, GMT may use a spherical approximation of the ellipsoid chosen, setting the flattening to zero, and using a mean radius. A warning will be given when this happens. If a different ellipsoid name than those mentioned here is given, GMT will attempt to parse the name to extract the semi-major axis (a in m) and the flattening. Formats allowed are:
a implies a zero flattening
a,inv_f where inv_f is the inverse flattening
a,b=b where b is the semi-minor axis (in m)
a,f=f where f is the flattening
This way a custom ellipsoid (e.g., those used for other planets) may be used. Further note that coordinate transformations in mapproject can also specify specific datums; see the mapproject man page for further details and how to view ellipsoid and datum parameters.
- PROJ_GEODESIC¶
Selects the algorithm to use for geodesic calculations. Choose between Vincenty, Rudoe, or Andoyer. The Andoyer algorithm is only approximate (to within a few tens of meters) but is up to 5 times faster. The Rudoe is given for legacy purposes. [default is Vincenty (accurate to about 0.5 mm)].
- PROJ_LENGTH_UNIT¶
Sets the default unit length. Choose between cm, inch, or point [default is c (or i)]. Note: In GMT, one point is defined as 1/72 inch (the PostScript definition), while it is often defined as 1/72.27 inch in the typesetting industry. There is no universal definition.)
- PROJ_MEAN_RADIUS¶
Applies when geodesics are approximated by great circle distances on an equivalent sphere or when surface areas are computed. Select from mean (R_1), authalic (R_2), volumetric (R_3), meridional, or quadratic [default is authalic].
- PROJ_SCALE_FACTOR¶
Changes the default map scale factor used for the Polar Stereographic [default is 0.9996], UTM [default is 0.9996], and Transverse Mercator [default is 1] projections in order to minimize areal distortion. Provide a new scale-factor or leave as default.
PostScript Parameters¶
- PS_CHAR_ENCODING¶
(static) Names the eight bit character set being used for text in files and in command line parameters. This allows GMT to ensure that the PostScript output generates the correct characters on the plot. Choose from Standard, Standard+, ISOLatin1, ISOLatin1+, and ISO-8859-x (where x is in the ranges 1-11 or 13-16). See Appendix F for details [default is ISOLatin1+ (or Standard+)]. Note: Normally the character set is written as part of the PostScript header. If you need to switch to another character set for a later overlay then you must use --PS_CHAR_ENCODING=encoding on the command line and not via gmt gmtset. Finally, note 6, 8, and 11 do not work with standard fonts.
- PS_COLOR_MODEL¶
Determines whether PostScript output should use RGB, HSV, CMYK, or GRAY when specifying color [default is rgb]. Note if HSV is selected it does not apply to images which in that case uses RGB. When selecting GRAY, all colors will be converted to gray scale using YIQ (television) conversion.
- PS_COMMENTS¶
(static) If true we will issue comments in the PostScript file that explain the logic of operations. These are useful if you need to edit the file and make changes; otherwise you can set it to false which yields a somewhat slimmer PostScript file [default is false].
- PS_CONVERT¶
Comma-separated list of optional module arguments that we should supply when psconvert is called implicitly under modern mode [A]. Ignored when psconvert is called on the command line explicitly. The option arguments must be listed without their leading option hyphen.
- PS_IMAGE_COMPRESS¶
Determines if PostScript images are compressed using the Run-Length Encoding scheme (rle), Lempel-Ziv-Welch compression (lzw), DEFLATE compression (deflate[,level]), or not at all (none) [default is deflate,5]. When specifying deflate, the compression level (1–9) may optionally be appended.
- PS_LINE_CAP¶
Determines how the ends of a line segment will be drawn. Choose among a butt cap where there is no projection beyond the end of the path, a round cap where a semicircular arc with diameter equal to the line-width is drawn around the end points, and square cap where a half square of size equal to the line-width extends beyond the end of the path [default is butt].
- PS_LINE_JOIN¶
Determines what happens at kinks in line segments. Choose among a miter join where the outer edges of the strokes for the two segments are extended until they meet at an angle (as in a picture frame; if the angle is too acute, a bevel join is used instead, with threshold set by PS_MITER_LIMIT), round join where a circular arc is used to fill in the cracks at the kinks, and bevel join which is a miter join that is cut off so kinks are triangular in shape [default is miter].
- PS_MEDIA¶
Classic mode: Sets the physical size of the current plotting paper [default is a4 (or letter)]. Modern mode: If user selects PostScript output then the above applies as well. For other graphics formats (PDF and rasters), the media size is determined automatically by cropping to fit the plot exactly (but see PS_CONVERT). However, if a specific media size is desired then the PS_MEDIA may be specified as well. The following formats (and their widths and heights in points) are recognized:
Media
width
height
Media
width
height
A0
2380
3368
archA
648
864
A1
1684
2380
archB
864
1296
A2
1190
1684
archC
1296
1728
A3
842
1190
archD
1728
2592
A4
595
842
archE
2592
3456
A5
421
595
flsa
612
936
A6
297
421
halfletter
396
612
A7
210
297
statement
396
612
A8
148
210
note
540
720
A9
105
148
letter
612
792
A10
74
105
legal
612
1008
B0
2836
4008
11x17
792
1224
B1
2004
2836
tabloid
792
1224
B2
1418
2004
ledger
1224
792
B3
1002
1418
B4
709
1002
B5
501
709
For a completely custom format (e.g., for large format plotters) you may also specify WxH, where W and H are in points unless you append a unit to each dimension (c, i, m or p [default is p]). Additional user-specific formats may be saved as separate line in a gmt_custom_media.conf file stored in ~/.gmt. Each record would have a format name followed by width and height of your media in points. For infinitely long paper rolls (e.g., plotters you can set height = 0).
- PS_MITER_LIMIT¶
Sets the threshold angle in degrees (integer in range [0,180]) used for mitered joins only. When the angle between joining line segments is smaller than the threshold the corner will be bevelled instead of mitered. [default is 35]. Setting the threshold angle to 0 implies the PostScript default of about 11 degrees. Setting the threshold angle to 180 causes all joins to be beveled.
- PS_PAGE_COLOR¶
Sets the color of the imaging background, i.e., the paper [default is white].
- PS_PAGE_ORIENTATION¶
(-P) Sets the orientation of the page. Choose portrait or landscape [default is landscape]. Only available in GMT classic mode.
- PS_SCALE_X¶
Global x-scale (> 0) to apply to plot-coordinates before plotting. Normally used to shrink the entire output down to fit a specific height/width [default is 1.0].
- PS_SCALE_Y¶
Global y-scale (> 0) to apply to plot-coordinates before plotting. Normally used to shrink the entire output down to fit a specific height/width [default is 1.0].
- PS_TRANSPARENCY¶
Sets the transparency mode to use when preparing PS for rendering to PDF. Choose from Color, ColorBurn, ColorDodge, Darken, Difference, Exclusion, HardLight, Hue, Lighten, Luminosity, Multiply, Normal, Overlay, Saturation, SoftLight, and Screen [default is Normal].
Calendar/Time Parameters¶
- TIME_EPOCH¶
Specifies the value of the calendar and clock at the origin (zero point) of relative time units (see TIME_UNIT). It is a string of the form yyyy-mm-ddT[hh:mm:ss] (Gregorian) or yyyy-Www-ddT[hh:mm:ss] (ISO) [default is 1970-01-01T00:00:00 (the origin of the UNIX time epoch)].
- TIME_INTERVAL_FRACTION¶
Determines if partial intervals at the start and end of an axis should be annotated. If the range of the partial interval exceeds the specified fraction of the normal interval stride we will place the annotation centered on the partial interval [default is 0.5].
- TIME_IS_INTERVAL¶
Used when input calendar data should be truncated and adjusted to the middle of the relevant interval. In the following discussion, the unit unit can be one of these time units: (y year, o month, u ISO week, d day, h hour, m minute, and s second). TIME_IS_INTERVAL can have any of the following three values: (1) OFF : no adjustment, time is decoded as given. (2) +nunit : activate interval adjustment for input by truncate to previous whole number of n units and then center time on the following interval. (3) -nunit. Same, but center time on the previous interval [default is off]. For example, with TIME_IS_INTERVAL =+1o, an input data string like 1999-12 will be interpreted to mean 1999-12-15T12:00:00.0 (exactly middle of December), while if TIME_IS_INTERVAL = off then that date is interpreted to mean 1999-12-01T00:00:00.0 (start of December).
- TIME_REPORT¶
Controls if a time-stamp should be issued at start of all progress reports. Choose among clock (absolute time stamp), elapsed (time since start of session), or none [default is none].
- TIME_SYSTEM¶
Shorthand for a combination of TIME_EPOCH and TIME_UNIT, specifying which time epoch the relative time refers to and what the units are. Choose from one of the preset systems below (epoch and units are indicated):
TIME_SYSTEM
TIME_EPOCH
TIME_UNIT
Notes
JD
-4713-11-25T12:00:00
d
Julian Date
MJD
1858-11-17T00:00:00
d
Modified Julian Date
J2000
2000-01-01T12:00:00
d
Astronomical time
S1985
1985-01-01T00:00:00
s
Altimetric time
UNIX
1970-01-01T00:00:00
s
UNIX time
RD0001
0001-01-01T00:00:00
s
RATA
0000-12-31T00:00:00
d
This parameter is not stored in the gmt.conf file but is translated to the respective values of TIME_EPOCH and TIME_UNIT.
- TIME_UNIT¶
Specifies the units of relative time data since epoch (see TIME_EPOCH). Choose y (year - assumes all years are 365.2425 days), o (month - assumes all months are of equal length y/12), d (day), h (hour), m (minute), or s (second) [default is s].
- TIME_WEEK_START¶
When weeks are indicated on time axes, this parameter determines the first day of the week for Gregorian calendars. (The ISO weekly calendar always begins weeks with Monday.) [default is Monday (or Sunday)].
- TIME_Y2K_OFFSET_YEAR¶
When 2-digit years are used to represent 4-digit years (see various FORMAT_DATEs), TIME_Y2K_OFFSET_YEAR gives the first year in a 100-year sequence. For example, if TIME_Y2K_OFFSET_YEAR is 1729, then numbers 29 through 99 correspond to 1729 through 1799, while numbers 00 through 28 correspond to 1800 through 1828. [default is 1950].